3.2.44 #
解答 #
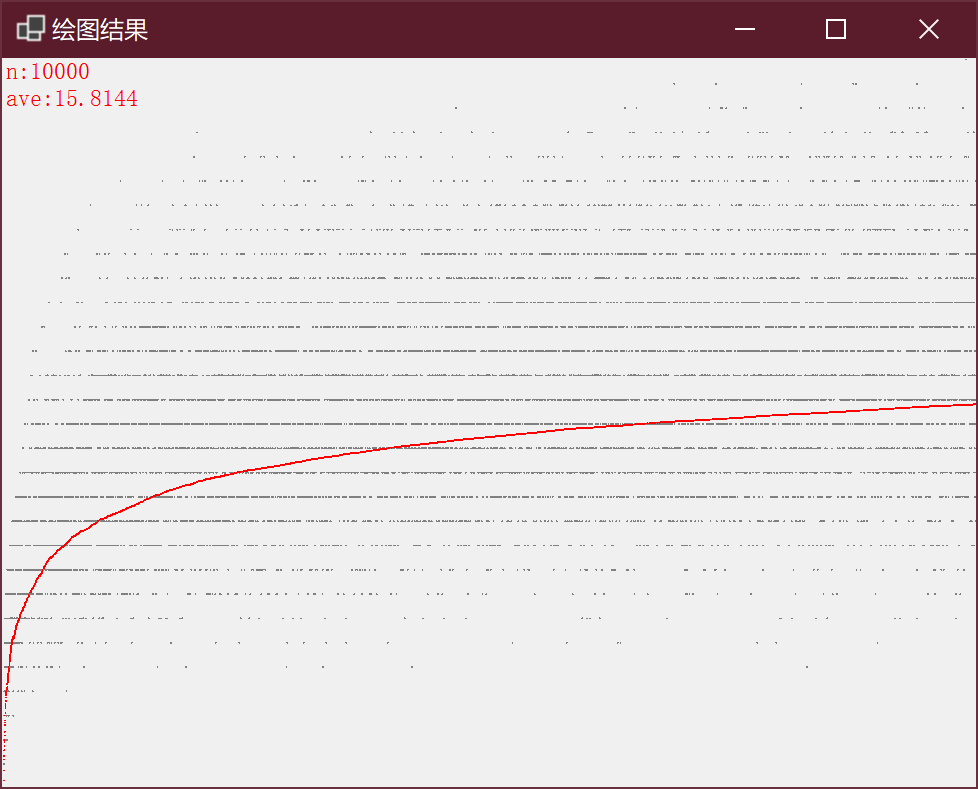
使用类似于 3.1.38 的方法进行绘图,当 n=10000 时的结果如下:
代码 #
绘图部分:
public void Draw(long[] data)
{
var panel = CreateGraphics();
var unitX = (float)ClientRectangle.Width / data.Length;
var unitY = (float)ClientRectangle.Height / data.Max();
var accumulation = 0f; // f = float
for (var i = 0; i < data.Length; i++)
{
// Gray
panel.FillEllipse(Brushes.Gray, (i + 1) * unitX, ClientRectangle.Bottom - data[i] * unitY, 2, 2);
// Red
panel.FillEllipse(Brushes.Red, (i + 1) * unitX, ClientRectangle.Bottom - accumulation / (i + 1) * unitY, 2, 2);
accumulation += data[i];
}
panel.DrawString($"n:{data.Length}\nave:{accumulation / data.Length}", SystemFonts.DefaultFont, Brushes.Red, 0, 0);
}
测试部分:
private long[] Test(int n)
{
var testCases = new long[n];
var testResult = new long[n];
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
testCases[i] = i;
}
Shuffle(testCases);
var bst = new BSTAnalysis<long, int>();
for (var i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
bst.CompareTimes = 0;
bst.Put(testCases[i], 1);
testResult[i] = bst.CompareTimes;
}
return testResult;
}
static void Shuffle<T>(T[] a)
{
var random = new Random();
for (var i = 0; i < a.Length; i++)
{
var r = i + random.Next(a.Length - i);
var temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[r];
a[r] = temp;
}
}